Last Updated on September 24, 2025
Understanding Suboxone Side Effects: A Comprehensive Guide
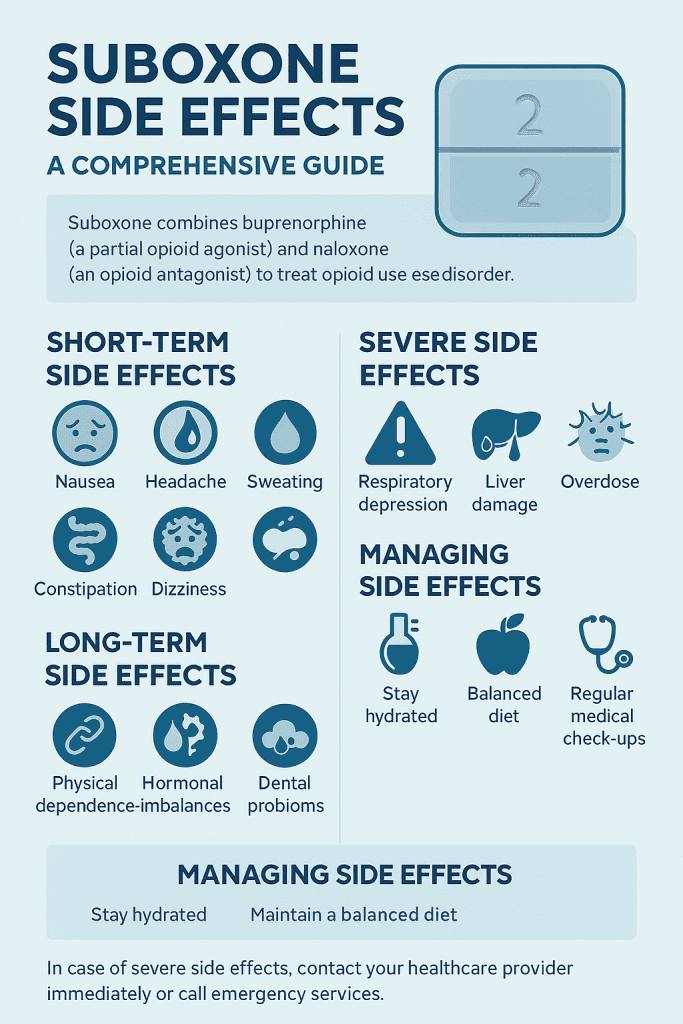
Suboxone, a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone, is a cornerstone in the treatment of opioid use disorder (OUD).While it offers significant benefits in managing withdrawal symptoms and cravings, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential side effects associated with its use. This guide delves into the common, severe, and long-term side effects of Suboxone, providing insights to help patients and healthcare providers navigate its use effectively.
What Is Suboxone?
Suboxone is a prescription medication formulated to assist individuals in overcoming opioid addiction. It combines buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist that alleviates withdrawal symptoms and cravings, with naloxone, an opioid antagonist that discourages misuse by precipitating withdrawal if the medication is injected . Administered sublingually, Suboxone is designed to be taken under the tongue, allowing for effective absorption and onset of action.
Short-Term Side Effects of Suboxone
While Suboxone is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience short-term side effects, especially during the initial stages of treatment. These can include:
-
Nausea and Vomiting: Commonly reported, these symptoms often subside as the body adjusts to the medication.
-
Headache: A frequent side effect that can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
-
Sweating: Increased perspiration may occur, particularly during the early phases of treatment.
-
Mouth Numbness or Burning Sensation: Due to the sublingual administration, some users report a temporary numbing effect in the mouth.
-
Constipation: A common opioid-related side effect, which can be mitigated with dietary adjustments or laxatives.
-
Lightheadedness or Dizziness: May occur, especially when standing up quickly, as the body adjusts to the medication.
-
Heart Palpitations: Some individuals may experience irregular heartbeats, which should be monitored.
-
Blurred Vision: Temporary visual disturbances can occur but typically resolve over time.
-
Back Pain: Musculoskeletal discomfort has been reported by some users.
-
Fainting: In rare cases, fainting may occur, necessitating medical attention.
-
Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or unusual sleep patterns may be experienced during treatment.
These side effects are generally transient and may diminish as the body becomes accustomed to Suboxone. However, if they persist or worsen, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider.
Severe Side Effects of Suboxone
Although rare, some individuals may experience more severe side effects that require immediate medical attention:
-
Respiratory Depression: Slowed or difficulty breathing can be life-threatening and necessitates urgent care.
-
Severe Allergic Reactions: Symptoms such as swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, and difficulty breathing require immediate medical intervention.
-
Liver Damage: Signs include yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), dark urine, and upper abdominal pain.
-
Adrenal Insufficiency: Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, nausea, and low blood pressure.
-
Heart Rhythm Problems: Irregular heartbeats or palpitations that are persistent or severe.
-
Overdose: Symptoms include extreme drowsiness, slow or difficult breathing, and loss of consciousness.
If any of these severe side effects occur, it’s critical to seek emergency medical care immediately.
Long-Term Side Effects of Suboxone
Long-term use of Suboxone can lead to chronic side effects, particularly if the medication is used beyond the recommended duration:
-
Physical Dependence: Over time, the body may become dependent on Suboxone, leading to withdrawal symptoms if the medication is discontinued abruptly.
-
Hormonal Imbalances: Long-term use can affect hormone levels, potentially leading to issues such as low libido or menstrual irregularities.
-
Dental Problems: Dry mouth and other oral health issues may arise, increasing the risk of dental decay and gum disease.
-
Cognitive Effects: Some individuals report memory problems or difficulty concentrating with prolonged use.
-
Mood Changes: Depression, anxiety, or irritability may occur, necessitating monitoring and possible intervention.
It’s essential for healthcare providers to regularly assess the need for continued Suboxone therapy and consider tapering strategies to minimize long-term risks.
Managing Suboxone Side Effects
To effectively manage the side effects of Suboxone:
-
Regular Monitoring: Healthcare providers should conduct routine assessments to monitor for side effects and adjust treatment as necessary.
-
Supportive Care: Addressing side effects such as constipation with dietary changes or medications can improve comfort.
-
Patient Education: Informing patients about potential side effects and encouraging open communication can lead to early detection and management of issues.
-
Tapering Plans: If discontinuation of Suboxone is appropriate, a gradual tapering plan can help mitigate withdrawal symptoms and reduce the risk of relapse.
If you’re planning a taper, review the expected buprenorphine withdrawal symptoms so you know what to expect and when to seek medical support.
Conclusion
Suboxone is a valuable tool in the treatment of opioid use disorder, offering significant benefits in managing withdrawal symptoms and cravings. However, it’s essential to be aware of the potential side effects, both short-term and long-term, associated with its use. By maintaining open communication with healthcare providers and adhering to prescribed guidelines, individuals can effectively manage these side effects and achieve a successful recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can Suboxone cause weight gain?
A1: Weight gain is not a commonly reported side effect of Suboxone. However, individual responses to medication can vary, and any unexpected changes should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Q2: Is it safe to take Suboxone during pregnancy?
A2: Suboxone is classified as a Category C medication during pregnancy, indicating that risk cannot be ruled out. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider to weigh the potential benefits and risks.
Q3: How long does it take for Suboxone to leave the system?
A3: The half-life of buprenorphine, the active ingredient in Suboxone, is approximately 24 to 60 hours. It may take several days for the medication to be eliminated from the body entirely.
Q4: Can Suboxone be used for pain management?
A4: While Suboxone is primarily used for opioid use disorder, buprenorphine, its active ingredient, is also used off-label for pain management in certain situations. Consult a healthcare provider for guidance.
Q5: What should I do if I miss a dose of Suboxone?
A5: If a dose is missed, take it as soon as remembered unless it’s close to the time for the next dose. Do not take two doses at once to make up for a missed dose. Consult a healthcare provider for specific instructions.
For more information or assistance with Suboxone treatment, consider reaching out to healthcare professionals or addiction specialists who can provide personalized guidance and support.
Source