Last Updated on August 27, 2025
Nicotine Detox Side Effects and Recovery: How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System?
Quitting nicotine is a significant step toward better health, but understanding the detox process is crucial. One common question among those trying to quit is, “How long does nicotine stay in your system?” The duration nicotine remains in the body can vary based on several factors, including the type of nicotine product used, frequency of use, and individual metabolism.
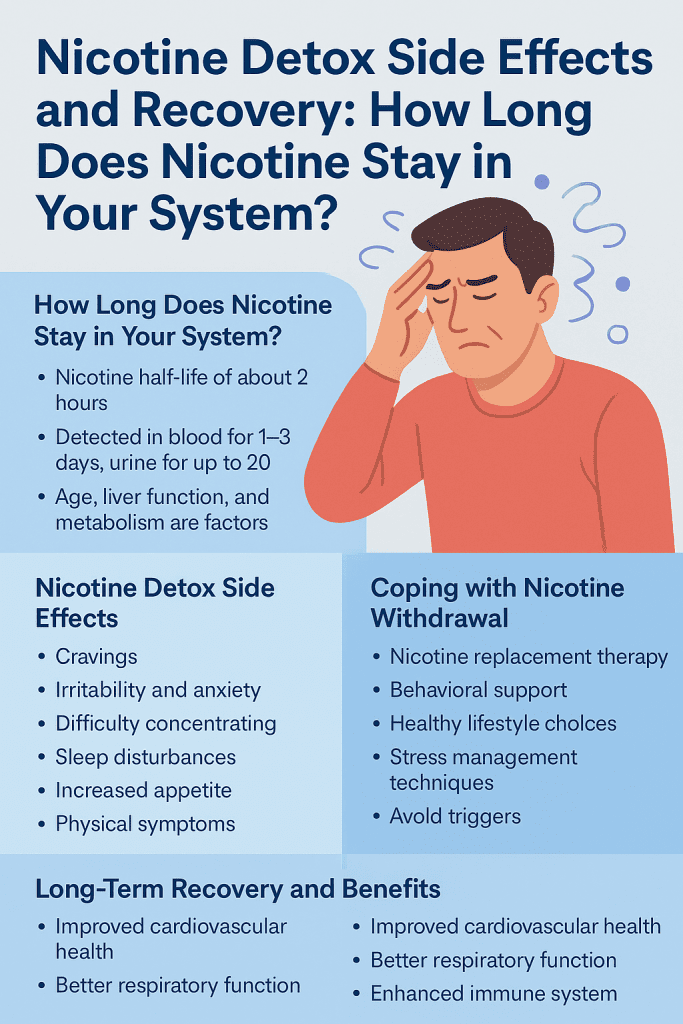
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System?
Nicotine is a highly addictive substance found in tobacco products and e-cigarettes. When you consume nicotine, it enters your bloodstream and is metabolized into various compounds, including cotinine. The time nicotine stays in your system depends on several factors:
-
Nicotine’s Half-Life: Nicotine has a half-life of approximately 2 hours, meaning half of the nicotine is eliminated from the body in that time. However, its metabolite, cotinine, has a longer half-life of about 16–40 hours, allowing it to be detected for a longer period .
-
Detection Times: The duration nicotine and cotinine can be detected varies by testing method:
-
Blood: Nicotine can be detected for 1–3 days; cotinine for up to 10 days.
-
Urine: Nicotine may be detectable for up to 20 days; cotinine for up to 30 days.
-
Saliva: Nicotine for 1–4 days; cotinine for up to 10 days.
-
Hair: Nicotine and cotinine can be detected for up to 90 days .
-
-
Individual Factors: Age, liver function, and metabolic rate can influence how quickly nicotine is cleared from the body.
Understanding these timelines can help you manage expectations during the detox process and prepare for potential withdrawal symptoms.
Nicotine Detox Side Effects
When you stop using nicotine, your body undergoes a detoxification process. This can lead to various withdrawal symptoms as your body adjusts to functioning without nicotine:
-
Cravings: A strong desire to use nicotine products.
-
Irritability and Anxiety: Emotional responses due to changes in brain chemistry.
-
Difficulty Concentrating: Cognitive challenges as the brain adapts.
-
Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns.
-
Increased Appetite: Often leading to weight gain.
-
Physical Symptoms: Headaches, dizziness, and gastrointestinal issues .
These symptoms typically peak within the first few days and gradually subside over 2–4 weeks. However, cravings and psychological symptoms may persist longer, varying from person to person.
Coping with Nicotine Withdrawal
Managing withdrawal symptoms is essential for a successful recovery. Here are some strategies to help you cope:
-
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): Products like patches, gum, and lozenges can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms by providing a controlled amount of nicotine without the harmful chemicals found in tobacco products.
-
Behavioral Support: Counseling, support groups, and quitlines can provide emotional support and coping strategies.
-
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can improve mood and energy levels.
-
Stress Management Techniques: Practices such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress and reduce the urge to smoke.
-
Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid situations or activities that trigger the urge to use nicotine.
Remember, the detox process is temporary, and the benefits of quitting far outweigh the challenges.
Long-Term Recovery and Benefits
The journey to recovery doesn’t end with detox. Long-term abstinence from nicotine leads to numerous health benefits:
-
Improved Cardiovascular Health: Reduced risk of heart disease and stroke.
-
Better Respiratory Function: Decreased risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer.
-
Enhanced Immune System: Lower susceptibility to infections.
-
Improved Mental Health: Reduced anxiety and depression over time.
-
Financial Savings: Significant cost savings from not purchasing nicotine products.
While the initial phase of quitting can be challenging, the long-term rewards are substantial.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How long does nicotine stay in your system after quitting smoking?
Nicotine can be detected in the blood for 1–3 days, while cotinine may remain detectable for up to 10 days .
Q2: What can speed up nicotine detox?
Staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy diet can support your body’s natural detoxification processes.
Q3: How can I tell if nicotine is still in my system?
Nicotine and cotinine levels can be measured through various tests, including blood, urine, saliva, and hair samples.
Q4: How long does nicotine withdrawal last?
Withdrawal symptoms typically peak within the first few days and subside over 2–4 weeks .
Q5: What are the best ways to cope with nicotine cravings during detox?
Utilizing NRT, engaging in physical activities, practicing relaxation techniques, and seeking support from healthcare professionals or support groups can help manage cravings.
Conclusion
Understanding how long nicotine stays in your system and the potential side effects of detoxification is crucial for anyone looking to quit nicotine. While the process may be challenging, the long-term health benefits are well worth the effort. If you’re considering quitting, consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan that suits your needs.
For additional support and resources, consider reaching out to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline at 1-800-662-HELP (4357) or visit findtreatment.gov.
Sources:
- National Institute on Drug Abuse. What is the scope of tobacco, nicotine, and e-cigarette use in the United States? | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Published May 2022. Accessed June 24, 2022. https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/tobacco-nicotine-e-cigarettes/what-scope-tobacco-use-its-cost-to-society
- Mayo Clinic. Nicotine dependence – Symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. Published April 19, 2022. Accessed June 24, 2022. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nicotine-dependence/symptoms-causes/syc-20351584
- Medline Plus. Emphysema. Published June 24, 2022. Accessed June 24, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/emphysema.html
- Seltman W. Age-Related Macular Degeneration. WebMD. Published November 22, 2021. Accessed June 24, 2022. https://www.webmd.com/eye-health/macular-degeneration/age-related-macular-degeneration-overview#1
- Mayo Clinic. Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) – Symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. Published May 20, 2022. Accessed June 24, 2022. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sudden-infant-death-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20352800
- Bahl R. Nicotine and Health Effects on the Body. Healthline. Published August 23, 2018. Accessed June 24, 2022. https://www.healthline.com/health-news/heres-how-nicotine-affects-the-body
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Nicotine. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US); 2014. Accessed June 24, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK294308/
- Peckham A. How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System? Healthline. Published May 11, 2022. Accessed June 24, 2022. https://www.healthline.com/health/quit-smoking/how-long-does-nicotine-stay-in-your-system
- American Cancer Society. Nicotine Replacement Therapy to Help You Quit Tobacco. Published August 2, 2021. Accessed June 24, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/healthy/stay-away-from-tobacco/guide-quitting-smoking/nicotine-replacement-therapy.html